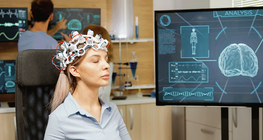
Our body is constantly receiving and processing information from the outside world through somatosensory system.
Inhalation therapy is a treatment for both acute and chronic obstructive airway diseases.
The first set of clinical examinations is the evaluation of the patient's vital signs.
Functionally the three main roles of the nervous system are sensation, integration, and response.
Motor tracts, motor neurons, and types of reflexes.
Effective management of patients with diabetes.
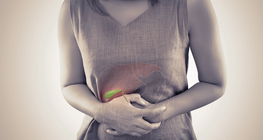
Understanding gallbladder and pancreatic disorders: treatment and management.
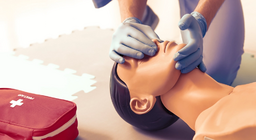
Resuscitation is the set of interventions and activities undertaken to restart the circulatory system after it has stopped.
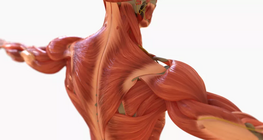
Striated muscle tissue, is one of the three types of muscle tissue present in the human body.
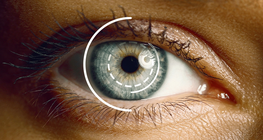
Visible electromagnetic radiation from the outside world is perceived by the visual system.
Diabetic emergencies must be recognised quickly and require prompt treatment.
An electrocardiogram is a simple, painless, non-invasive screening test.
External stimuli are perceived and transmitted to the brain through specific sensory organs.
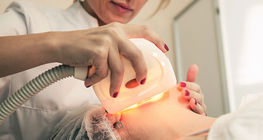
Low-laser therapy is a non-invasive light source treatment used in physiotherapy.
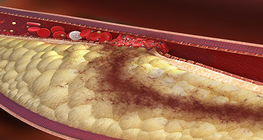
The narrowing of the peripheral arteries causes a decrease in the blood supply of the area.
Sensing chemical stimuli from the outside world requires receptors in the olfactory and taste organs.
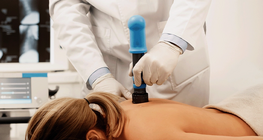
Shockwave therapy represents a form of mechanotherapy.
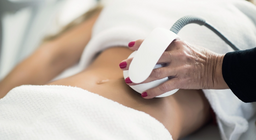
Deep oscillation therapy is an electro-mechanic therapy procedure in which a pulsating electrostatic field is built up between the probe and the tissue.
Sleeping interrupts the periods when we are awake.
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for maintaining the body's physiologic processes.