ในบทเรียนนี้ คุณจะได้เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับประวัติ โครงสร้าง และการใช้กล้องจุลทรรศน์แบบใช้แสง
ข้อมูลที่เรียบง่ายและตรงไปตรงมาเกี่ยวกับการแพร่ระบาดของโคโรนาไวรัส
บทเรียนนี้นำเสนอโครงสร้างและการจำแนกแบคทีเรียและบทบาทของแบคทีเรียในชีวิตของเรา
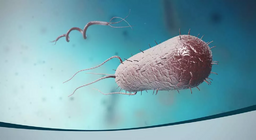
Bacteria occur in a wide range of shapes, including spheres, rods and spirals.
ไมโทซิส เป็นกระบวนการที่เซลล์ยูคาริโอต แบ่งออกเป็นสองเซลล์ และจำนวนโครโมโซม ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง
เซลล์สืบพันธุ์ของเรา เป็นเซลล์เดี่ยว ที่ผลิตจากเซลล์ดิพลอยด์ (เซลล์ที่มีโครโมโซม 2 ชุด) โดยการไมโอซิส ซึ่งเป็นการแบ่งเซลล์แบบพิเศษ
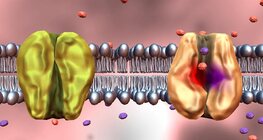
This animation explains active and passive transport processes occurring through cell membranes
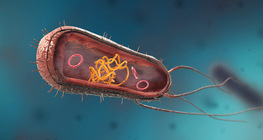
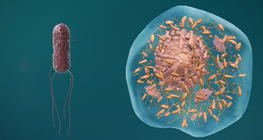
Bacteria are unicellular organisms that have no nuclei and are a few micrometres in length.
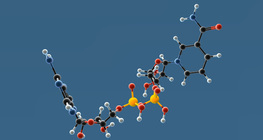
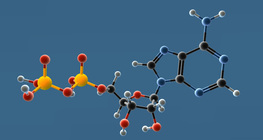
NAD⁺ is a coenzyme that plays an important role mainly in catabolic processes, while NADP is important in anabolic processes as hydrogen carriers.
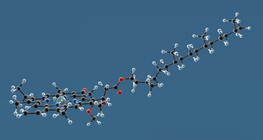
Chlorophyll is a photosensitive green pigment found in plants; it absorbs light energy, thus plays a vital role in photosynthesis.
Enzymes are protein molecules catalysing biochemical reactions. Their activity can be regulated.
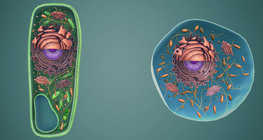
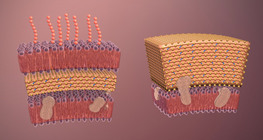
There are two basic cell types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
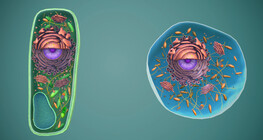
Typical plant and animal cells exhibit a number of similarities and differences.
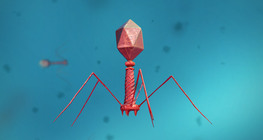
Viruses consist of protein and DNA or RNA; they reprogram infected cells to produce more viruses.
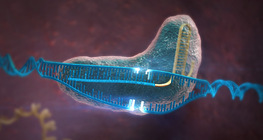
Genome editing is a type of genetic engineering which results in changes in the genome of an organism. This animation presents one of the best-known genome editing protocols, the CRISPR/Cas9 system.